Kubernetes 101 : Storage : Persistent volumes (PV) and Persistent Volume Claim (PVC)
Persistent Volume Clain ( PVC ) allows application running inside a pod to request storage ( Persistent volumes ) without worrying about the underlying technology.
The task of providing storage that fits the application will be in hands of the kubernetes administrator.
The task of providing storage that fits the application will be in hands of the kubernetes administrator.
Persistent volumes are not attached to the life-cycle of the pods that use them, they persist even if the pod exits or crashes.
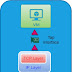
Persistent volume claim and persistent volumes:
A PVC is a request for storage.
The PVC specifies the amount of storage a pod needs and also the access rights needed for the storage.
Kubernetes tries to find the most suitable PV that matches the characteristics of a PVC.
The characteristics of the PV must match or be greater than what the PVC requires.
Remark:
The PVCs must exist in the same namespace as the pods attached to it.
Pods mount a PVCs in the same way they would mount a volume.
Pods mount a PVCs in the same way they would mount a volume.
Deleting a PVC:
Once the PVC is deleted, the storage space associated with the PV is reclaimed by kubernetes.
The reclaim policies:
Below are the reclaim policies:
- Retain: the PV is not reclaimed by kubernetes after the PVC is deleted
- Delete: kubernetes deletes the PVC along with the storage attached to the PV
Persistent volume configuration file:
We create a storage "persistent volume" on the host to be mounted on the "hostPath" path and to be used later by pods, after requesting it through a PVC.
Below are the different access modes for the Persistent volumes:
- ReadWriteOnce (RWO) : the volume can be mounted in read-write mode by one nodes.
- ReadWriteOnce (RWX) : the volume can be mounted in read-write mode by many nodes.
- ReadOnlyMany (ROX) : the volume can be mounted in read-only mode by many nodes.
We notice that the status is still "available" because it is not bound to any PVC ( CLAIM ).
Remark:
After the persistent volume claim is created kubernetes binds the persistent volume claim to a "matching" persistent volume.
The persistent volume claim:
Below is a Yaml configuration file for a PVC:
Below is a Yaml configuration file for a PVC:
We create the persistent volume claim from the Yaml file using the below command:
We can check our created persistent volume using the below command:
We notice that the status is "bound" and the claim is "default/pvc_1".
The "default" is the default namespace.
A pod configuration file and its PVC:
Below is the pod configuration file with the persistent volume claim ( PVC ) to request storage ( PV ):
We can create our pod using the below command:


















Comments